1856-1943
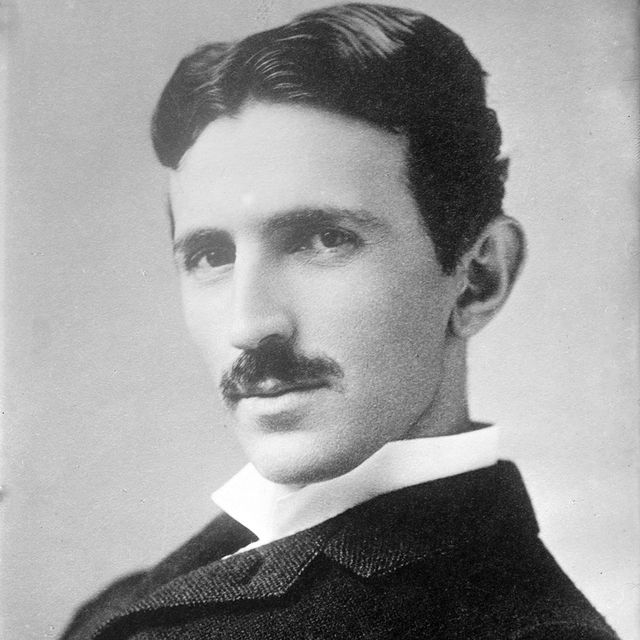
Who Was Nikola Tesla?
Engineer and inventor Nikola Tesla designed the alternating-current (AC) electric system, which is the predominant electrical system used across the world today. He also created the “Tesla coil” that is still used in radio technology. Born in modern-day Croatia, Tesla immigrated to the United States in 1884 and briefly worked with Thomas Edison before the two parted ways. The Serbian American sold several patent rights, including those to his AC machinery, to George Westinghouse. Tesla died at age 86 in January 1943, but his legacy lives on through his inventions and the electric car company Tesla that’s named in his honor.
Quick Facts
FULL NAME: Nikola Tesla
BORN: July 10, 1856
DIED: January 7, 1943
BIRTHPLACE: Smiljan, Croatia
ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Cancer
When Was Nikola Tesla Born?
Tesla was born on July 10, 1856, in the Austrian Empire town of Smiljan that is now part of Croatia.
He was one of five children, including siblings Dane, Angelina, Milka, and Marica. Nikola’s interest in electrical invention was spurred by his mother, Djuka Mandic, who invented small household appliances in her spare time while her son was growing up.
Tesla’s father, Milutin Tesla, was a Serbian orthodox priest and a writer, and he pushed for his son to join the priesthood. But Nikola’s interests lay squarely in the sciences.
Tesla received quite a bit of education. He studied at the Realschule, Karlstadt (later renamed the Johann-Rudolph-Glauber Realschule Karlstadt) in Germany; the Polytechnic Institute in Graz, Austria; and the University of Prague during the 1870s.
Nikola Tesla and Thomas Edison
After university, Tesla moved to Budapest, Hungary, where for a time he worked at the Central Telephone Exchange. It was while in Budapest that the idea for the induction motor first came to Tesla, but after several years of trying to gain interest in his invention, at age 28, Tesla decided to leave Europe for America.
In 1884, Tesla arrived in the United States with little more than the clothes on his back and a letter of introduction to famed inventor and business mogul Thomas Edison, whose DC-based electrical works were fast becoming the standard in the country. Edison hired Tesla, and the two men were soon working tirelessly alongside each other, making improvements to Edison’s inventions.
Several months later, the two parted ways due to a conflicting business-scientific relationship, attributed by historians to their incredibly different personalities. While Edison was a power figure who focused on marketing and financial success, Tesla was commercially out-of-touch and somewhat vulnerable. Their feud would continue to affect Tesla’s career.
Solo Venture
In 1885, Tesla received funding for the Tesla Electric Light Company and was tasked by his investors to develop improved arc lighting. After successfully doing so, however, Tesla was forced out of the venture and, for a time, had to work as a manual laborer in order to survive. His luck changed two years later when he received funding for his new Tesla Electric Company.
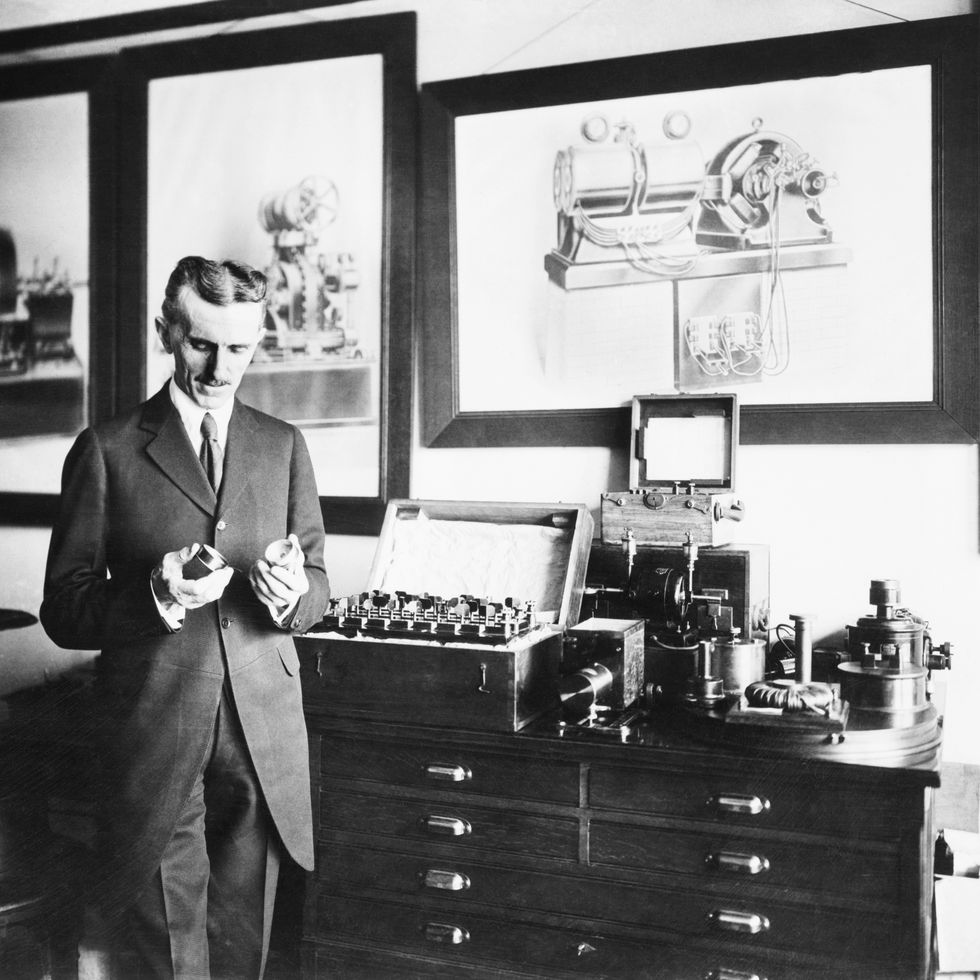
Inventions
Throughout his career, Tesla discovered, designed, and developed ideas for a number of important inventions—most of which were officially patented by other inventors—including dynamos (electrical generators similar to batteries) and the induction motor.
He was also a pioneer in the discovery of radar technology, X-ray technology, remote control, and the rotating magnetic field—the basis of most AC machinery. Tesla is most well-known for his contributions in AC electricity and for the Tesla coil.
AC Electrical System
Tesla designed the alternating-current (AC) electrical system, which quickly became the preeminent power system of the 20th century and has remained the worldwide standard ever since. In 1887, Tesla found funding for his new Tesla Electric Company, and by the end of the year, he had successfully filed several patents for AC-based inventions.
Tesla’s AC system soon caught the attention of American engineer and businessman George Westinghouse, who was seeking a solution to supplying the nation with long-distance power. Convinced that Tesla’s inventions would help him achieve this, in 1888, he purchased his patents for $60,000 in cash and stock in the Westinghouse Corporation.
As interest in an AC system grew, Tesla and Westinghouse were put in direct competition with Thomas Edison, who was intent on selling his direct-current (DC) system to the nation. A negative press campaign was soon waged by Edison, in an attempt to undermine interest in AC power.
Unfortunately for Edison, the Westinghouse Corporation was chosen to supply the lighting at the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, and Tesla conducted demonstrations of his AC system there.
Hydroelectric Power Plant
In 1895, Tesla designed what was among the first AC hydroelectric power plants in the United States, at Niagara Falls. The following year, it was used to power the city of Buffalo, New York—a feat that was highly publicized throughout the world and helped further AC electricity’s path to becoming the world’s power system.
Tesla Coil
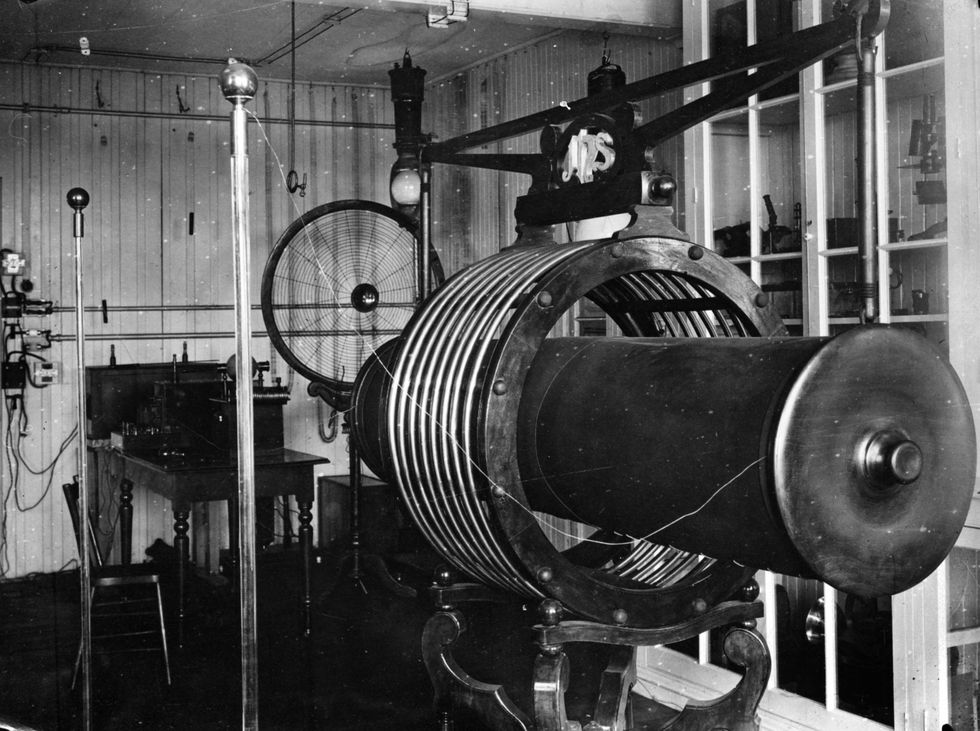
In the late 19th century, Tesla patented the Tesla coil, which laid the foundation for wireless technologies and is still used in radio technology today. The heart of an electrical circuit, the Tesla coil is an inductor used in many early radio transmission antennas.
The coil works with a capacitor to resonate current and voltage from a power source across the circuit. Tesla used his coil to study fluorescence, x-rays, radio, wireless power, and electromagnetism in the earth and its atmosphere.
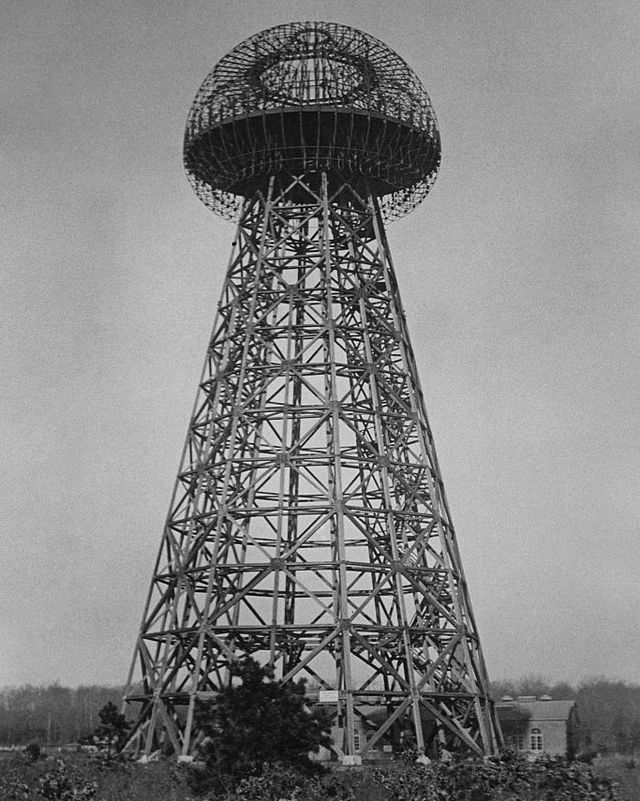
Wireless Power and Wardenclyffe Tower
Having become obsessed with the wireless transmission of energy, around 1900, Tesla set to work on his boldest project yet: to build a global, wireless communication system transmitted through a large electrical tower that would enable information sharing and provide free energy throughout the world.
With funding from a group of investors that included financial giant J. P. Morgan, Tesla began work on the free energy project in earnest in 1901. He designed and built a lab with a power plant and a massive transmission tower on a site on Long Island, New York, that became known as Wardenclyffe.
However, doubts arose among his investors about the plausibility of Tesla’s system. As his rival, Guglielmo Marconi—with the financial support of Andrew Carnegie and Thomas Edison—continued to make great advances with his own radio technologies, Tesla had no choice but to abandon the project.
The Wardenclyffe staff was laid off in 1906, and by 1915, the site had fallen into foreclosure. Two years later, Tesla declared bankruptcy, and the tower was dismantled and sold for scrap to help pay the debts he had accrued.
Death Ray
After suffering a nervous breakdown following the closure of his wireless power project, Tesla eventually returned to work, primarily as a consultant. But as time went on, his ideas became progressively more outlandish and impractical. He grew increasingly eccentric, devoting much of his time to the care of wild pigeons in the parks of New York City. Tesla even drew the attention of the FBI with his talk of building a powerful “death ray,” which had received some interest from the Soviet Union during World War II.
How Did Nikola Tesla Die?
Poor and reclusive, Tesla died of coronary thrombosis on January 7, 1943, at the age of 86 in New York City, where he had lived for nearly 60 years.
Legacy: Movies, Electric Car, and Wardenclyffe Tower Renovation
The legacy of Tesla’s work lives on to this day. In 1994, a street sign identifying “Nikola Tesla Corner” was installed near the site of his former New York City laboratory, at the intersection of 40th Street and 6th Avenue.
Several movies have highlighted Tesla’s life and famous works, most notably:
- The Secret of Nikola Tesla, a 1980 biographical film starring Orson Welles as J. P. Morgan.
- Nikola Tesla, The Genius Who Lit the World, a 1994 documentary produced by the Tesla Memorial Society and the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade, Serbia.
- The Prestige, a 2006 fictional film about two magicians directed by Christopher Nolan, with rock star David Bowie portraying Tesla.
In 2003, a group of engineers founded Tesla Motors, a car company named after Tesla dedicated to building the first fully electric-powered car. Entrepreneur and engineer Elon Musk contributed over $30 million to Tesla in 2004 and serves as the company’s co-founder and CEO.
Tesla Motors unveiled its first electric car, the Roadster, in 2008. A high-performance sports vehicle, the Roadster helped changed the perception of what electric cars could be. In 2014, Tesla launched the Model S, a lower-priced model that, in 2017, set the MotorTrend world record for 0 to 60 miles per hour acceleration at 2.28 seconds. The company’s designs showed that an electric car could have the same performance as gasoline-powered sports car brands like Porsche and Lamborghini.
Tesla Science Center at Wardenclyffe
Since Tesla’s original forfeiture of his free energy project, ownership of the Wardenclyffe property has passed through numerous hands. Several attempts have been made to preserve it, but efforts to declare it a national historic site failed in 1967, 1976, and 1994.
Then, in 2008, a group called the Tesla Science Center (TSC) was formed with the intention of purchasing the property and turning it into a museum dedicated to the inventor’s work. In 2009, the Wardenclyffe site went on the market for nearly $1.6 million, and for the next several years, the TSC worked diligently to raise funds for its purchase. In 2012, public interest in the project peaked when Matthew Inman of TheOatmeal.com collaborated with the TSC in an Internet fundraising effort, ultimately receiving enough contributions to acquire the site in May 2013.
Wardenclyffe Tower finally joined the National Register of Historic Places in 2018. Work on its restoration is still in progress. A $20 million redevelopment broke ground in April 2023, but those efforts were complicated by large fire that November. The site is closed to the public “for the foreseeable future” for reasons of safety and preservation, according to the Tesla Science Center.
Quotes
- Our virtues and our failings are inseparable, like force and matter. When they separate, man is no more.
- I do not think you can name many great inventions that have been made by married men.
- The scientists of today think deeply instead of clearly. One must be sane to think clearly, but one can think deeply and be quite insane.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us!
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us